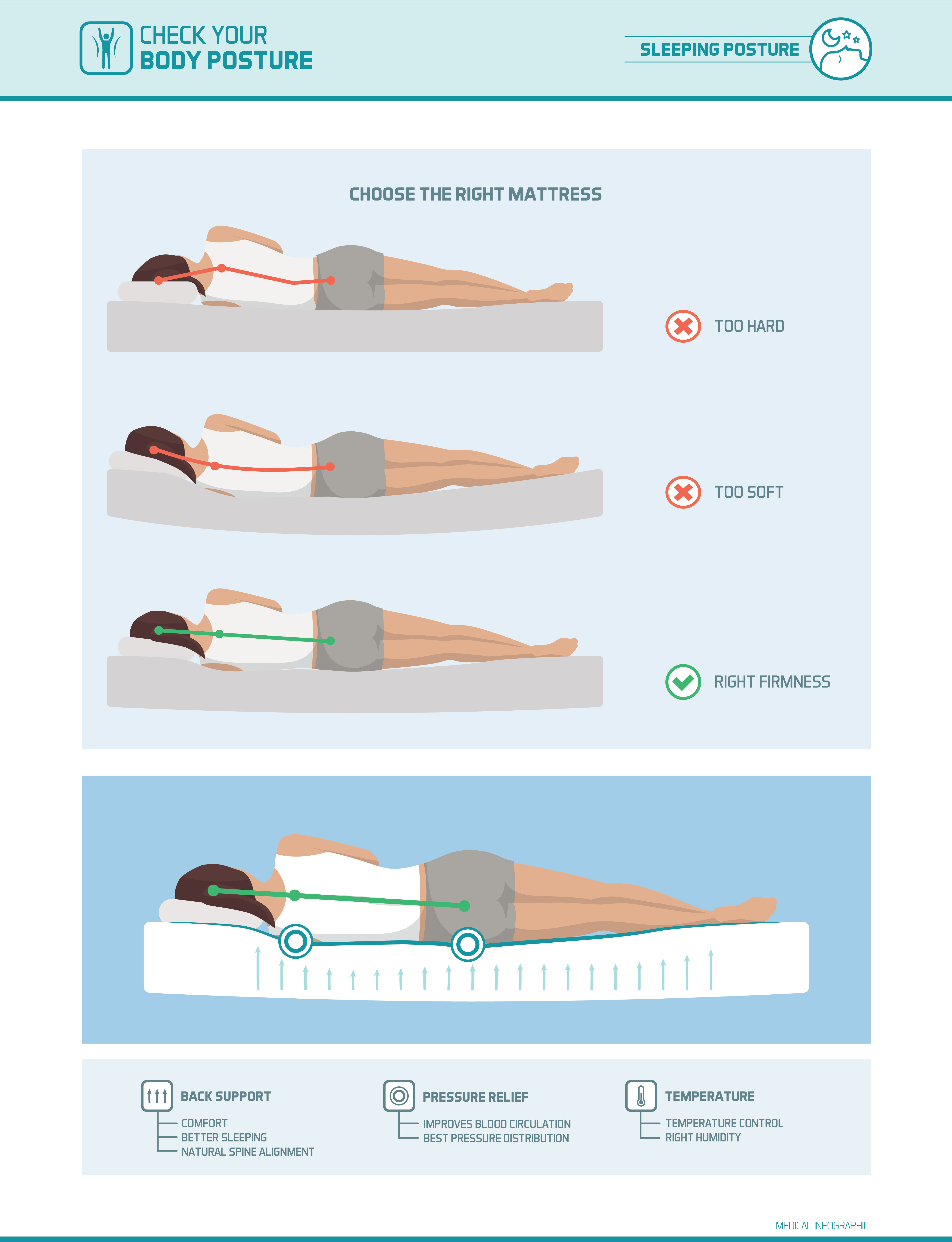
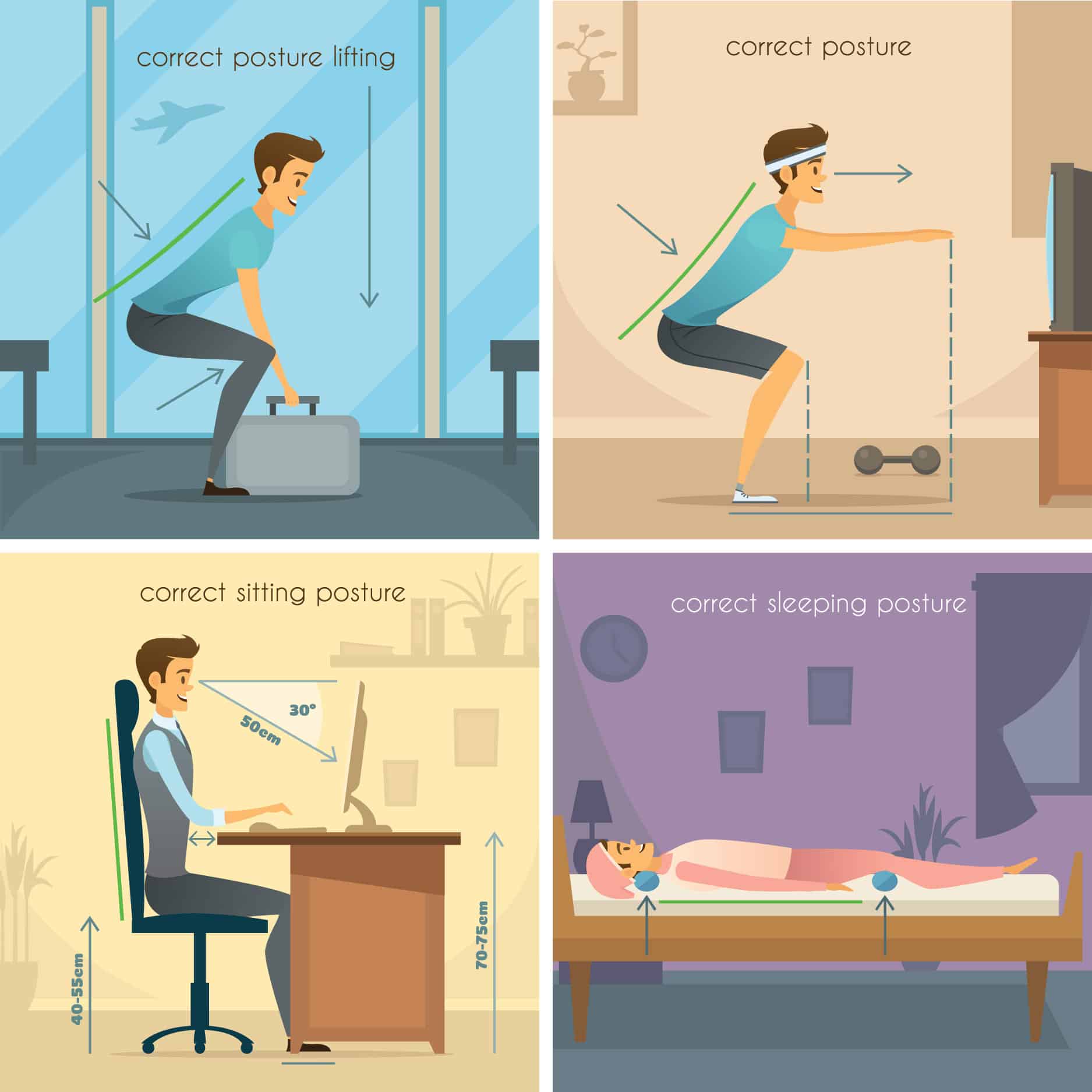
Good sitting posture is among the most overlooked aspects of overall well-being and quality of life. This is such a shame as the habits of proper posture are easy to adopt and its effects contribute to an easier life. Just think of the physical and psychological benefits that come with sitting well, from watching television to working at your desk job, even when driving your car.
The Benefits of Good Sitting Posture
Good posture means keeping your body upright against gravity in a way that puts the least possible strain on your ligaments, joints and muscles, especially on your spine. When you have developed it with practice, you will enjoy the following benefits that emphasize its importance in quality of life:
- It keeps your bones and joints in their proper alignment.
- It aids in decreasing the premature wear and tear of your joint surfaces that otherwise can result in bone-related injuries and illnesses (e.g., arthritis).
- It prevents the spine, especially its bones, in abnormal positions that can otherwise increase the risks of injuries and illnesses, such as herniated discs.
- It significantly reduces the severity, duration and frequency of back pain and muscle tension from the shoulders to the hips.
- It contributes to a better physical appearance (i.e., you look and feel more confident).
The bottom line: When you sit well, you are more likely to work well and live well! You will find that, indeed, good sitting posture has a significant impact on your life.
The Requirements of Good Sitting Posture
Keep in mind that for your initial tries at proper sitting posture, you have to make a conscious decision to do so. You have to be both aware of your body’s position and willing to correct it, when necessary. You will soon discover that proper posture becomes more of a habit and less of a conscious decision over time.
The basics in proper sitting posture are:
- Sit up with your back as straight as possible. Your shoulders should be back, your buttocks must touch the back of the chair, and your back should be relaxed without slouching.
- Use a lumbar roll (i.e., a small round pillow) or a rolled-up towel to support your lower back, if necessary.
- Be relaxed while sitting down since muscle tension is possible when you’re as stiff as a board.
You have to be aware that the natural gentle S-curve of your spine from your neck to your tailbone should be present, too.
If you’re not using a lumbar roll, you can keep these tips in mind to find the best possible sitting position:
- Sit at the end of the chair and adopt a slouching posture.
- Draw yourself up as straight as possible so that the curve of your back is highlighted.
- Hold it for a few seconds.
- Relax (i.e., release) your position but only slightly so that you now have a proper sitting posture.
But it isn’t just your back that contributes to good sitting posture. You must also ensure that:
- Your body weight is evenly distributed on both hips.
- Your knees are bent at a right angle and your knees are either even with or slightly higher than your hip level.
- You should avoid crossing your legs but keep your feet flat on the floor.
When you’re at your desk, you should also keep these tips in mind:
- Adjust your workstation and chair height for proper posture purposes.
- Rest your arms and elbows either on your desk or chair.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed.
- Keep your eyes level with your computer screen.
Every 25 minutes, you are well-advised to get up and stretch for at least 30 seconds.